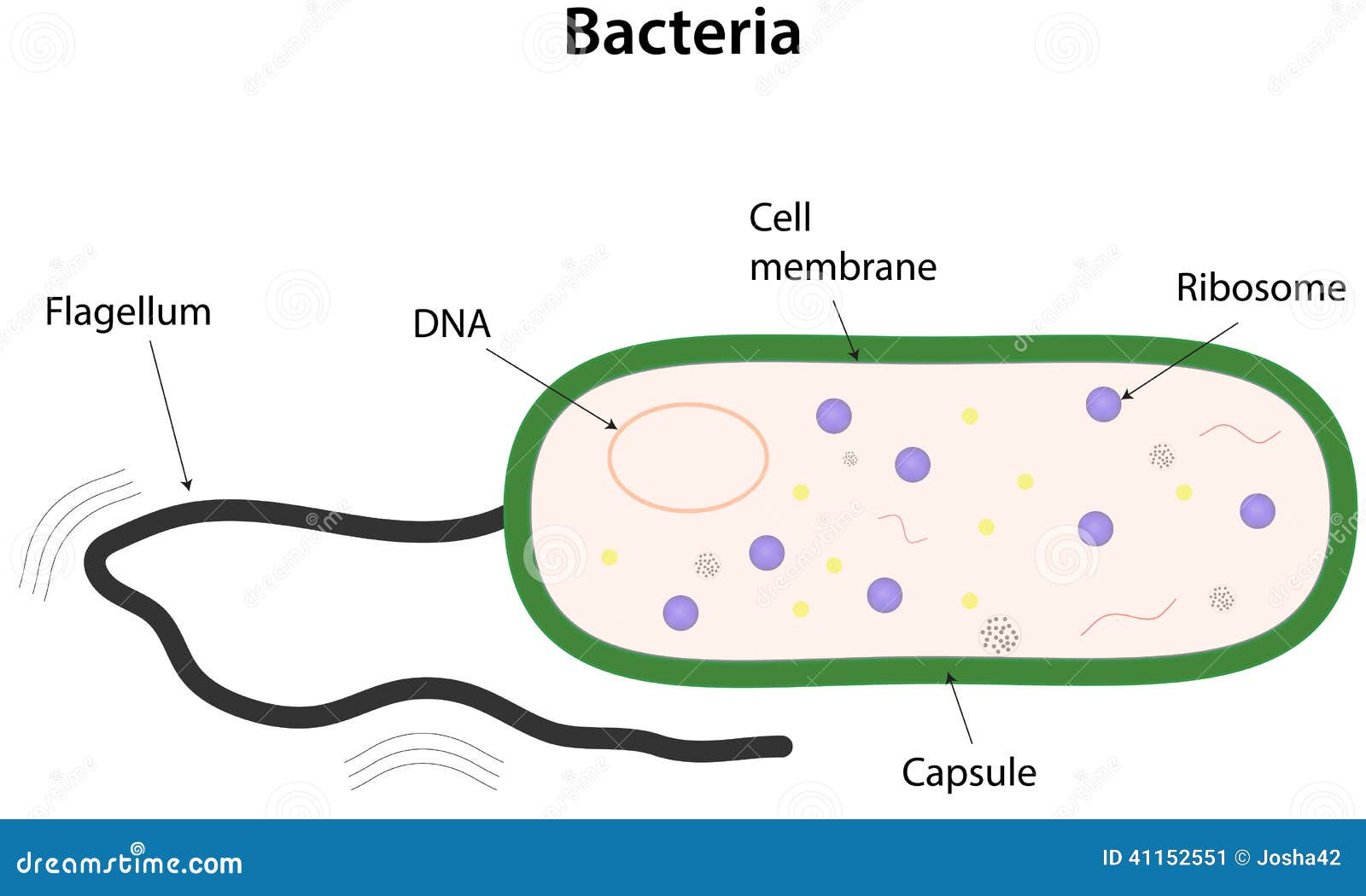
Bacteria stock vector. Illustration of bacteria, ribosome 41152551
Bacteria Diagram with Labels Bacterial cells have simpler internal structures like Pilus (plural Pili), Cytoplasm, Ribosomes, Capsule, Cell Wall, Plasma membrane, Plasmid, Nucleoid, Flagellum, etc. Labeled Bacteria diagram Eukaryotes have been shown to be more recently evolved than prokaryotic microorganisms.

Bacterial Cell Diagrams 101 Diagrams
bacteria, any of a group of microscopic single-celled organisms that live in enormous numbers in almost every environment on Earth, from deep-sea vents to deep below Earth's surface to the digestive tracts of humans. Bacteria lack a membrane-bound nucleus and other internal structures and are therefore ranked among the unicellular life-forms.

Bacterial cell structure Year 12 Human Biology
Bacteria Diagram representing the Structure of Bacteria Ultrastructure of a Bacteria Cell The structure of bacteria is known for its simple body design. Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms with the absence of the nucleus and other c ell organelles; hence, they are classified as prokaryotic organisms.
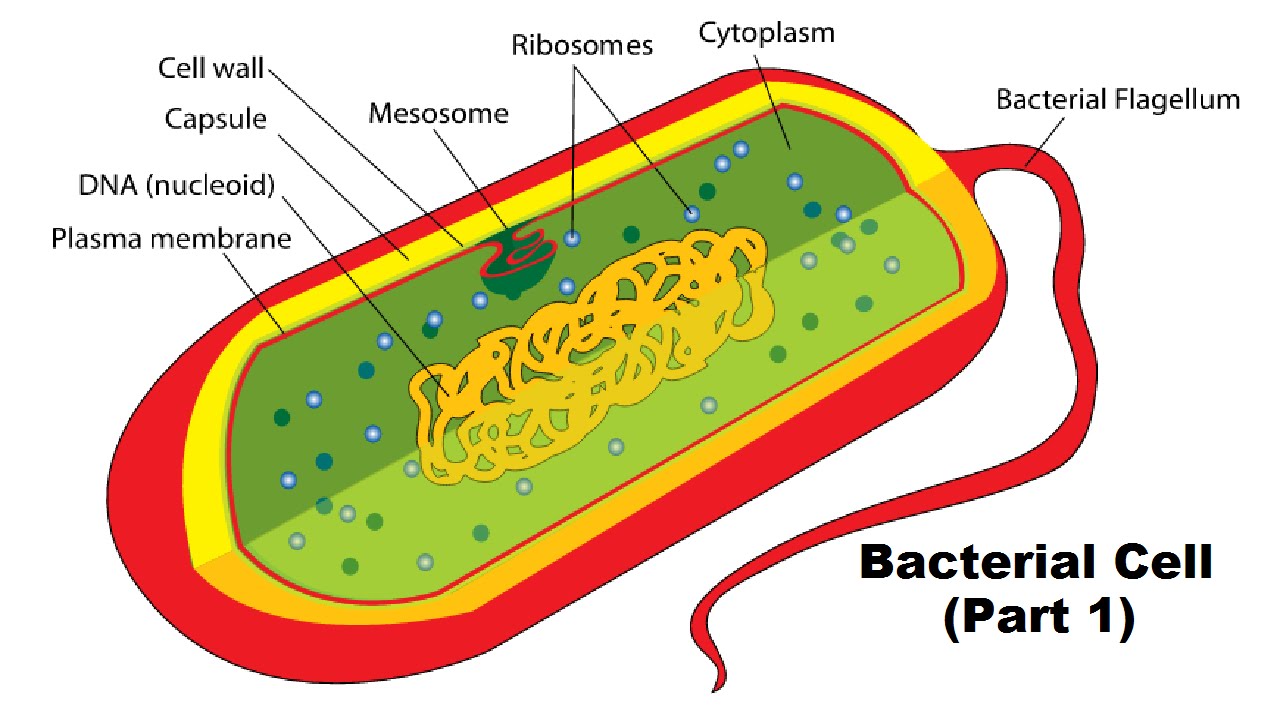
Structure of a Bacterial Cell (Part 1) YouTube
Key points: Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms belonging to the domains Bacteria and Archaea. Prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells, have no nucleus, and lack organelles. All prokaryotic cells are encased by a cell wall. Many also have a capsule or slime layer made of polysaccharide.
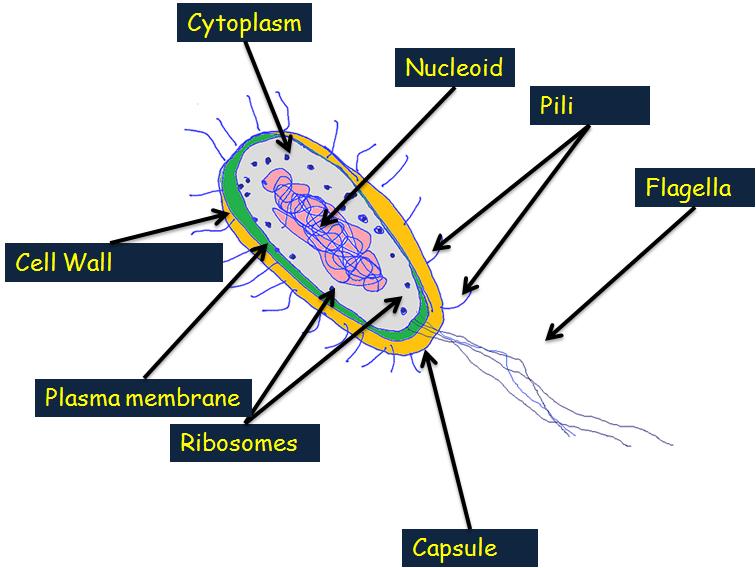
Bacterial Cell Labelled Diagram ClipArt Best
Bacterium Cell Anatomy Activity Key 1. Flagellum 2. Capsule 3. Cell wall 4. Cell membrane 5. Cytosol 6. Ribosome 7. Pili 8. Plasmid 9. Nucleoid (DNA) Title: Bacterial Cell Coloring Page Author: Ask A Biologist Subject: Bacteria Cell Parts Keywords: Bacteria cell anatomy, cells, bacterium

Bacterial Cell Diagrams 101 Diagrams
In this video, we show you how to draw and label a basic bacterial cell. Check out http://eacharya.tumblr.com for more!

Structure and Function of Prokaryotic Cells
Shape and Arrangement-1 Cocci (s., coccus) - spheres diplococci (s., diplococcus) - pairs streptococci - chains staphylococci - grape-like clusters tetrads - 4 cocci in a square sarcinae - cubic configuration of 8 cocci Shape and Arrangement-2 bacilli (s., bacillus) - rods coccobacilli - very short rods

Bacterial Structure Plantlet
These can rotate or move in a whip-like motion to move the bacterium. Plant and bacterial cell walls provide structure and protection. Only plant cell walls are made from cellulose. The DNA of.
Effective use of alcohol for aromatic blending Tisserand Institute
The bacteria shapes, structure, and labeled diagrams are discussed below. Table of Contents [ show] Sizes The sizes of bacteria cells that can infect human beings range from 0.1 to 10 micrometers. Some larger types of bacteria such as the rickettsias, mycoplasmas, and chlamydias have similar sizes as the largest types of viruses, the poxviruses.
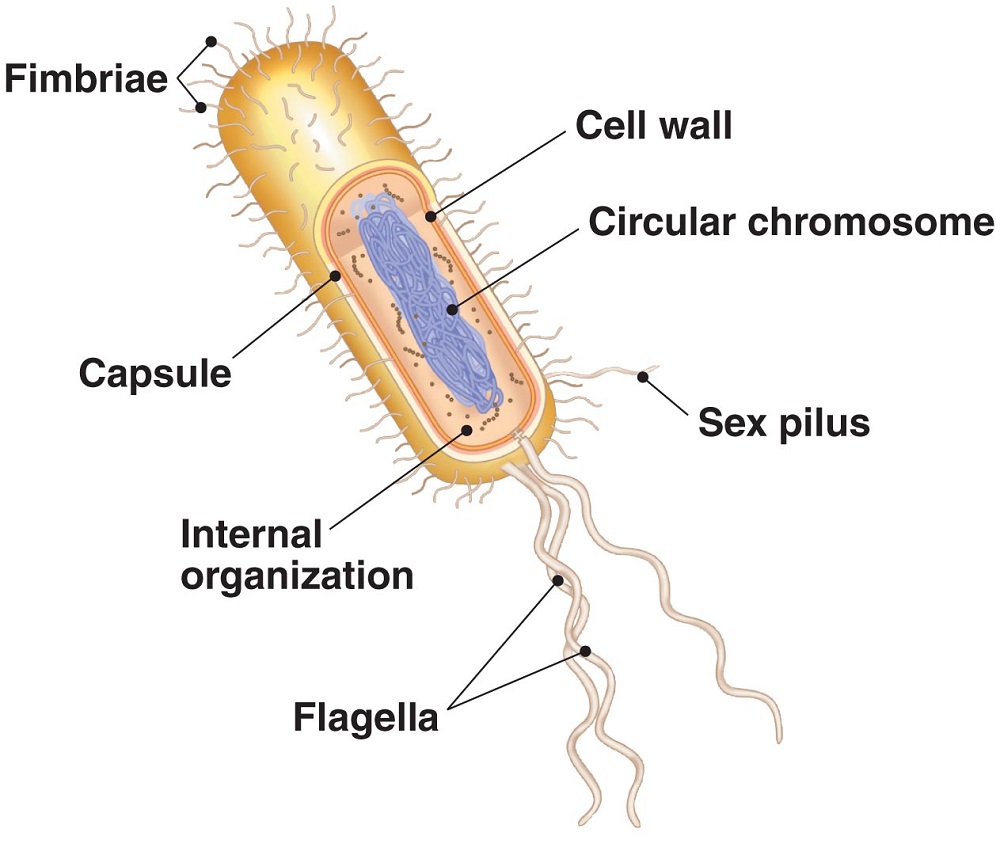
Bacterial Cell Diagrams 101 Diagrams
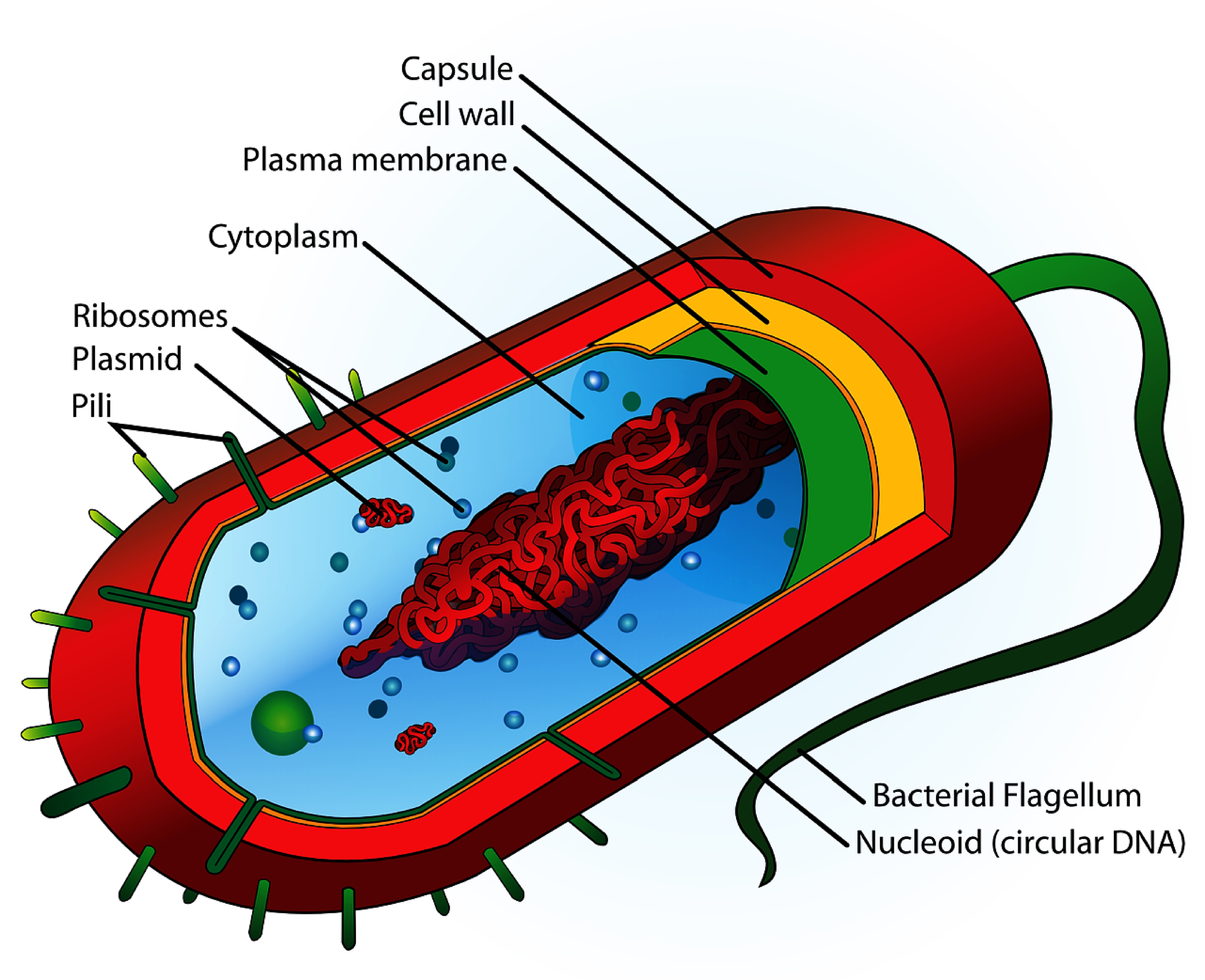
The components are: 1. Cell Envelope 2. Cytoplasm 3. Nucleoid 4. Plasmids 5. Inclusion Bodies 6. Flagella 7. Pili and Fimbriae. Bacterial Cell: Component # 1. Cell Envelope: It is the outer covering of protoplasm of bacterial cell. Cell envelope consists of 3 components— glycocalyx, cell wall and cell membrane. (i) Glycocalyx (Mucilage Sheath):

Picture Prokaryotic cell, Cell structure, Bacterial cell structure
The schematic diagram of bacterial cell structure is shown in the Fig.1.The bacteria possess the morphological structures for the purpose of performing some physiological functions, e.g. flagella.

Label the Bacterial Cell Key New Unit 1 Cells and Cell Processes Ppt Cell processes, Cell wall
In gram-negative bacteria, the cell wall is thin and releases the dye readily when washed with an alcohol or acetone solution. Cytoplasm - The cytoplasm, or protoplasm, of bacterial cells is where the functions for cell growth, metabolism, and replication are carried out. It is a gel-like matrix composed of water, enzymes, nutrients, wastes.
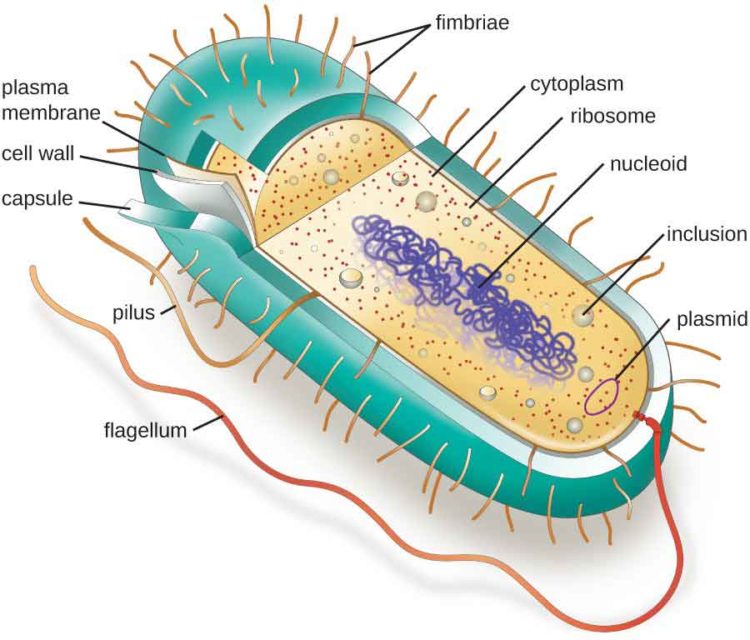
Bacterial Cell Structure and Function
A prokaryote is a simple, single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
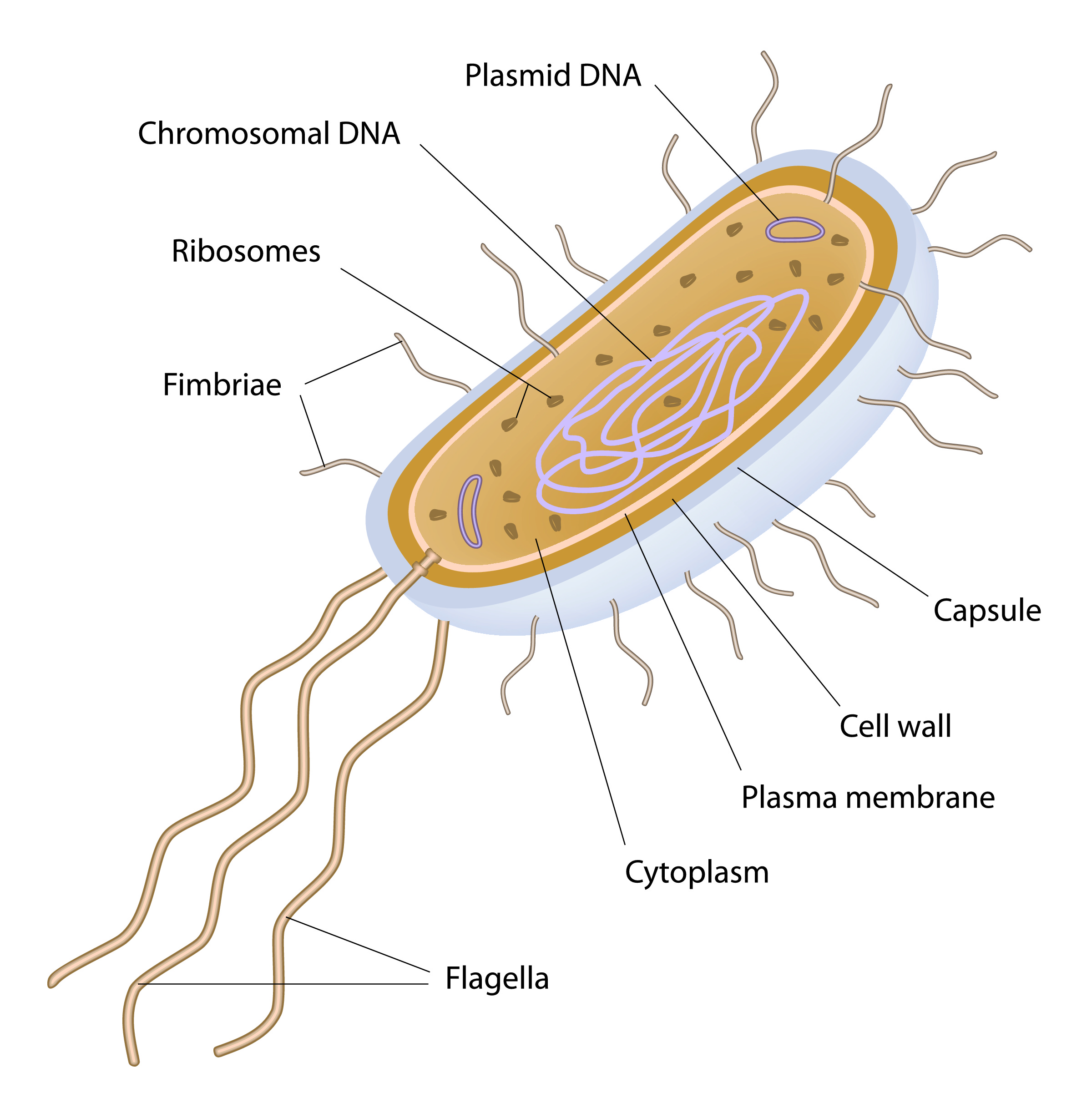
Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes worksheet from EdPlace
Bacteria (sing. bacterium) are unicellular prokaryotic microorganisms which divide by binary fission. They do not possess nuclear membrane and the nucleus consists of a single chromosome of circular double-stranded DNA helix (Fig. 1.1). Flagella: ADVERTISEMENTS:
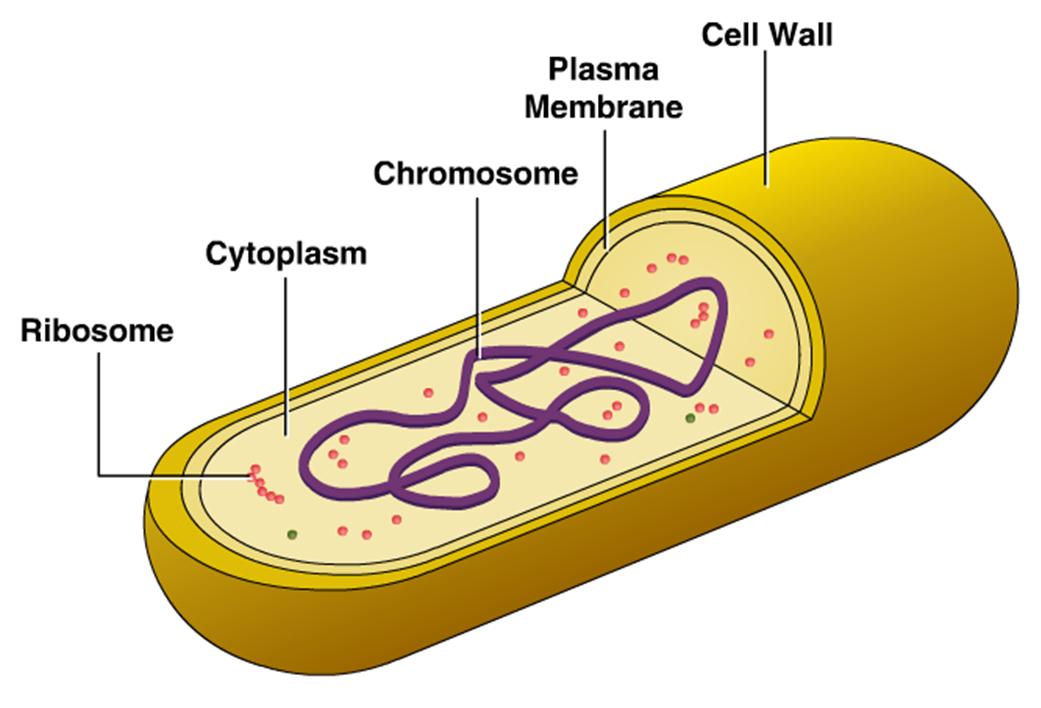
Cellular Structure of Bacteria ZeroInfections
August 14, 2021. Bacteria are unicellular. Their structure is a very simple type. Bacteria are prokaryotes because they do not have a well-formed nucleus. A typical bacterial cell is structurally very similar to a plant cell. The cell structure of a bacterial cell consists of a complex membrane and membrane-bound protoplast.

Page 1
Bacterial cell have simpler internal structure. It lacks all membrane bound cell organelles such as mitochondria, lysosome, golgi, endoplasmic reticulum, chloroplast, peroxisome, glyoxysome, and true vacuole. Bacteria also lacks true membrane bound nucleus and nucleolus. The bacterial nucleus is known as nucleoid.